E Law Resources Causation

The rules of causation state that the claimant has to prove that the defendants breach of duty was the factual cause of material damage when considering the facts of barnett v chelsea kensington hospital management committee ckhmc where the claimants husband became ill after drinking tea which had arsenic when taken to hospital the doctor in the casualty department did not examine him.
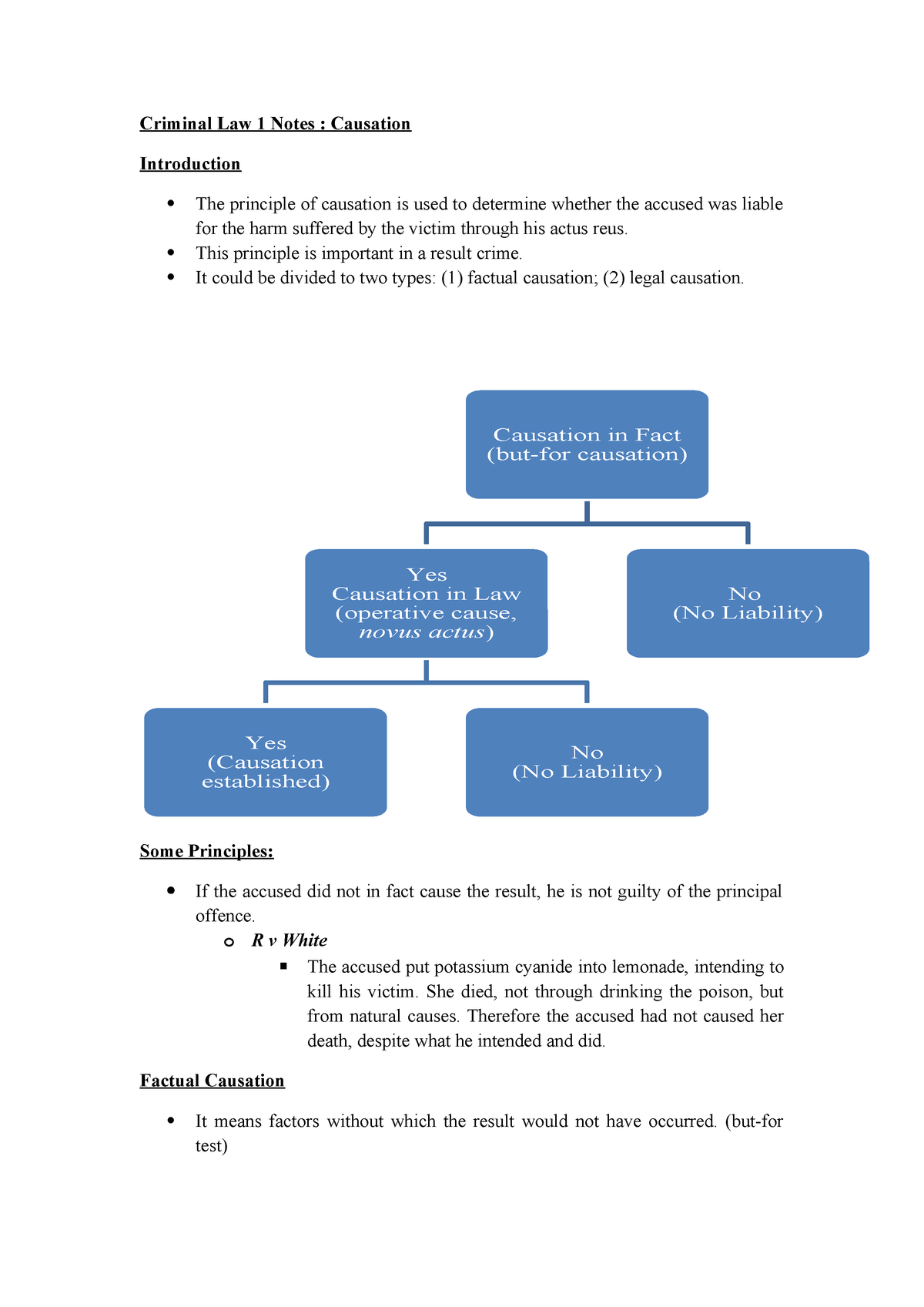
E law resources causation. In most cases a simple application of the but for test will resolve the question of causation in tort law ie but for the defendant s actions would the claimant have suffered the loss. In barnett v chelsea and kensington management committee 1956 ac 613 the courts found that because injury to the claimant would have occurred regardless of the defendant s conduct there was no factual causation. In the case of pagett for example the morally reprehensible actions of the police were held to be no more than an intervening act and pagett was deemed liable for the death of the girl. Causation in criminal liability is divided into factual causation and legal causation factual causation is the starting point and consists of applying the but for test.
Do you know the difference between factual causation and legal causation. Quiz on causation criminal law revisionhow much do you know about causation in criminal liability. What is a chain of causation. Do you know what novus actus interveniens means and how it applies to causation.
Causation is shaped by public policy and too often the decision of the courts reflects the need to protect institutions such as hospitals and the police. If yes the defendant is not liable. In negligence cases which are among the most popular types of cases in the legal system there are four parts that law students try to cram into their brains before an exam. Matters of causation are decided on the balance of probabilities i e.
And hughes and legal causation explaining the de minimis rule intervening acts such as the actions of a third party and the victims own act. Causation in criminal law is concerned with whether the defendant s conduct contributed sufficiently to the prohibited consequence to justify the criminal liability which would be assessed from two aspects namely factual and legal causation. To demonstrate causation in tort law the claimant must establish that the loss they have suffered was caused by the defendant. What is a chain of causation and how may this be broken.
In most instances where there exist no complicating factors. Causation refers to the enquiry as to whether the defendant s conduct or omission caused the harm or damage causation must be established in all result crimes. Do you know the approaches used where there is more than one possible cause and what a novus actus interveniens means in relation to causation in tort law. The all or nothing approach and the burden of proof.
This resource discusses the concept of factual and legal causation by explaining the but for test using relevant case examples i e. For a plaintiff to succeed in a negligence case the defendant must have owed a duty of care to the plaintiff. Duty breach causation and damages let s break those down and specifically talk about the third one.