Malaysian Legal System Notes

Functions classifications and divisions 2 1 introduction 2 2 definition of law 2 2 1 juristicdefinition 2 2 2 statutory definition.
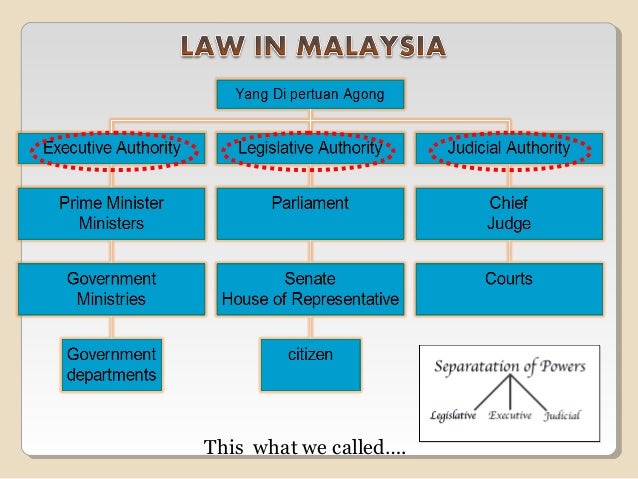
Malaysian legal system notes. The legislature the executive and the judiciary in common with other parliamentary democracies such as the united kingdom. A procedure or process for interpreting and enforcing the law. Generally any law which is inconsistent with the federal constitution is invalid. When malaysian judges accept such principles they become part of malaysian common law and malaysian law has developed in that manner.
This note is not endorsed by any parties. Three main types of legal systems in the world. Malaysia is a federation of 13 states and 3 federalterritories. And it has a federal constitution and a 13 state constitutions federal constitution is the supreme law of the land.
Legal systems in asean. The malaysian parliament functions under a written constitution and is governed by it. The federal constitution is the supreme law of the land. Malaysian courts have a wide discretion whether to accept the common law principle or not.
State constitution is law made by state to govern her own state. The federal constitution is the supreme law of the land. The government is comprised of three arms. Generally any law which is inconsistent with the federal constitution is invalid.
Law 033 chp 1 legal system definition. The distinction 1 4 malaysian legal system. Article 121 1a islamic legal system. It is a predominantly common law country with a separate islamic law system.
Sivabalan v straits times. Updated prior 2nd edition 2019. An introduction 1 1 law and legal system 1 2 malaysian legal history 1 3 colony and a protectorate or protected state. Almost all ex british colonies have adopted the common law system.
Latifah bte mat zin v rosmawati bte sharibun anor. Malaysia s legal system comprises laws which have arise from three significant periods in malaysian history dating from the malacca sultanate to the spread of islam to southeast asia and following the absorption into the indigenous culture of british colonial rule which introduced a constitutional government and the common law. Some topic is incomplete add it yourself. Malaysia open access from the asean law association.
The principal law making body is parliament. Its law making power is limited by the provisions in the constitution. Its law making power is limited by the provisions in the constitution. Malaysia practises a parliamentary democracy and has a constitutional monarchy just as the united kingdom.